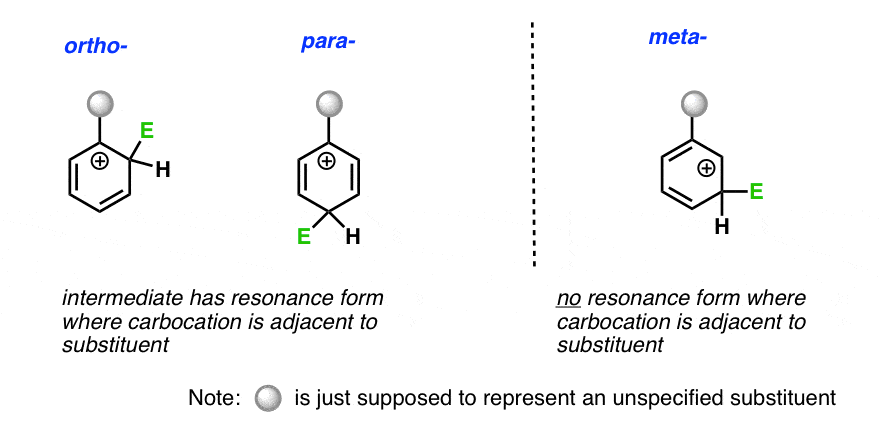
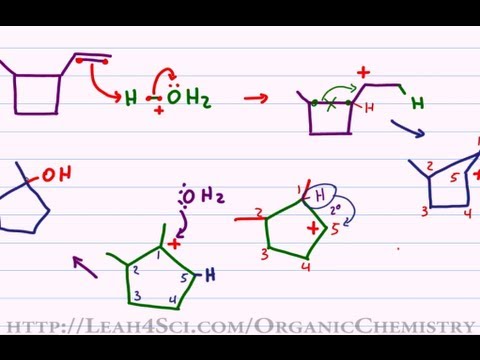
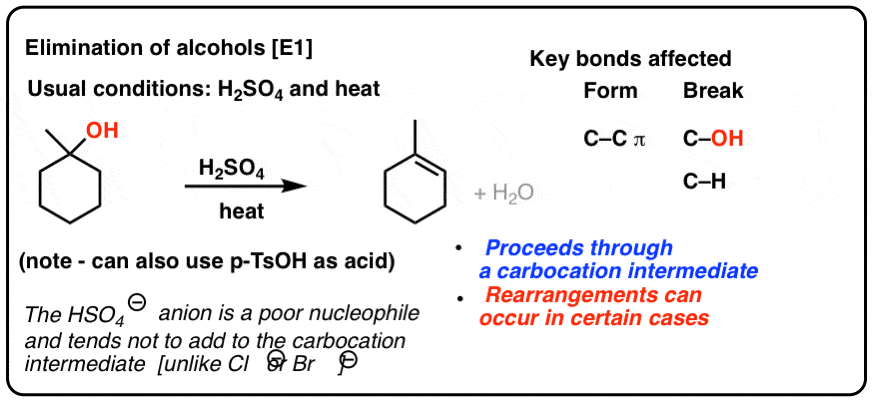
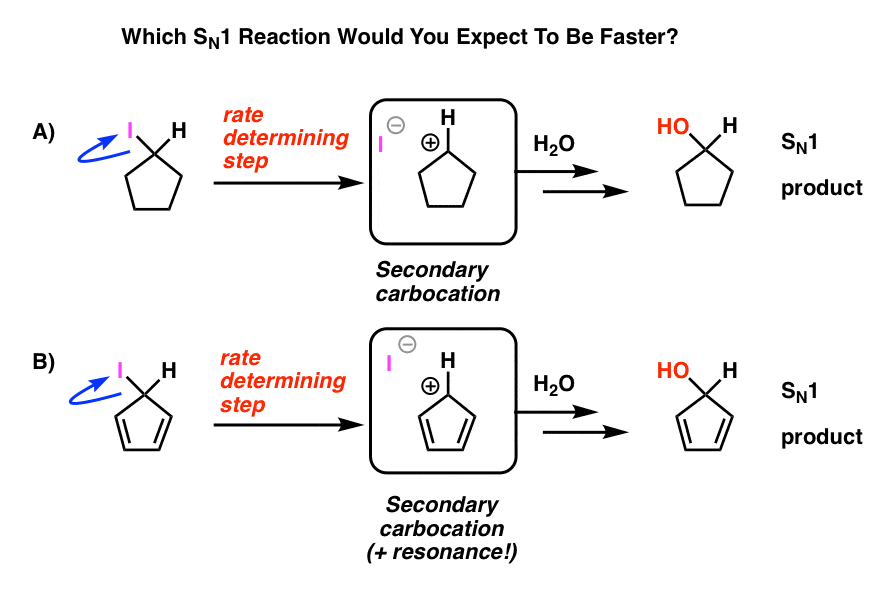
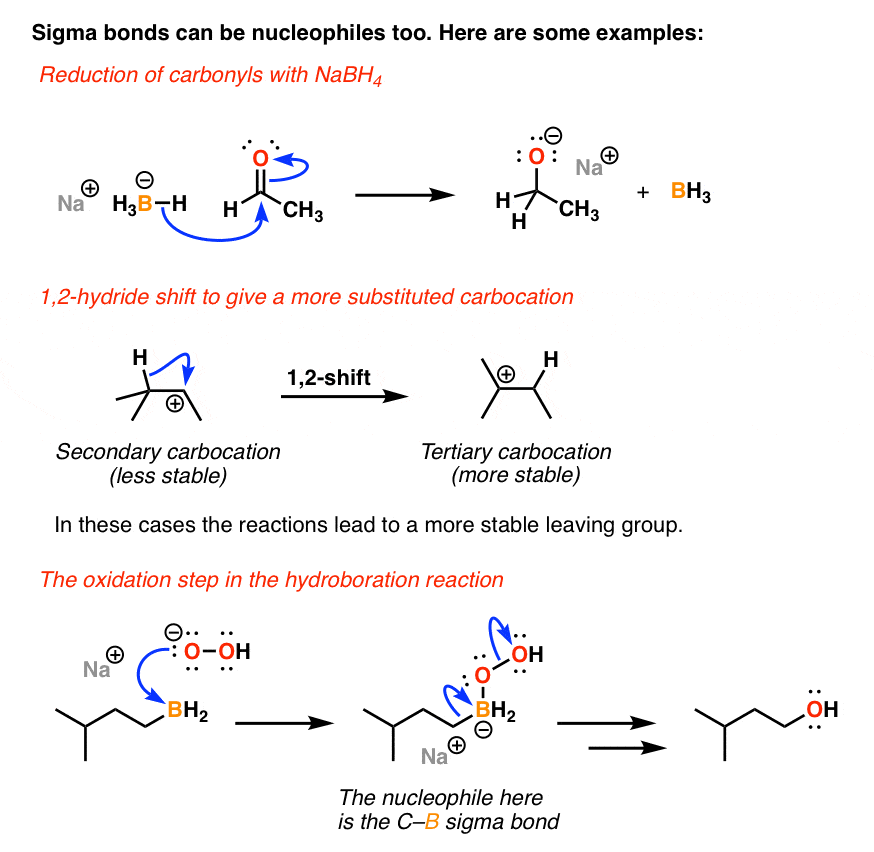
Any trivalent disubstituted carbon is generally a vinylic carbocation in which the carbon atom which is bearing the positive charge is found to be double bonded and will always exist as sp hybridized.
Vinylic carbocation resonance structures.
When the leaving group leaves the carbon for which it was attached becomes sp 2 hybridized with an empty p.
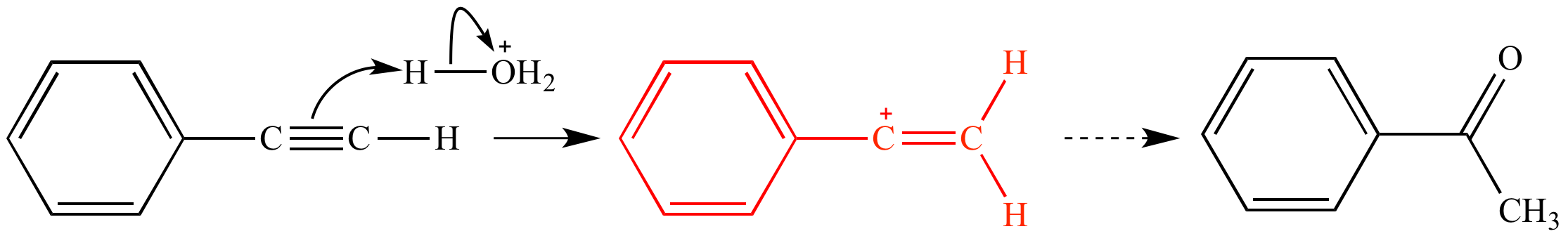
Acid catalyzed hydration of phenyl acetylene a terminal alkyne involves a vinylic carbocation intermediate.
This carbocation is also a benzylic carbocation.
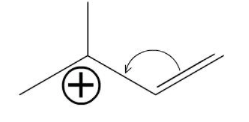
This delocalization stablizes the allyl carbocation making it more stable than a normal primary carbocation.
This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to determine which carbocation is most stable.
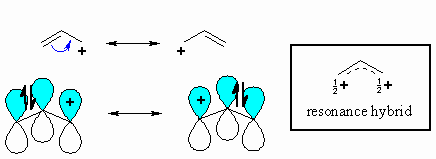
An allylic carbocation is a resonance stabilized carbocation in each of the two resonance forms of which the formal charge of 1 is on an allylic carbon.
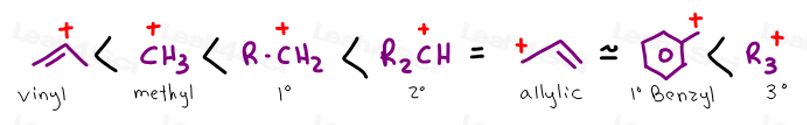
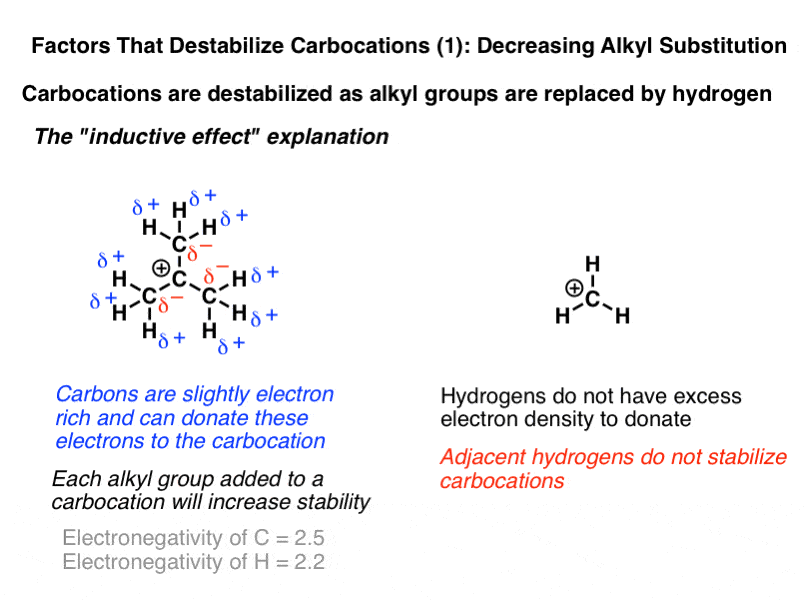
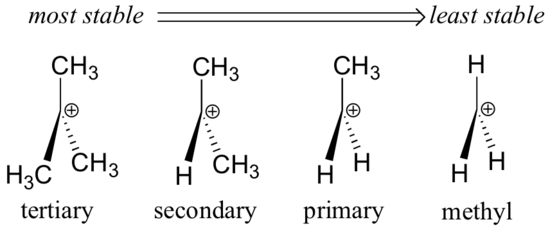
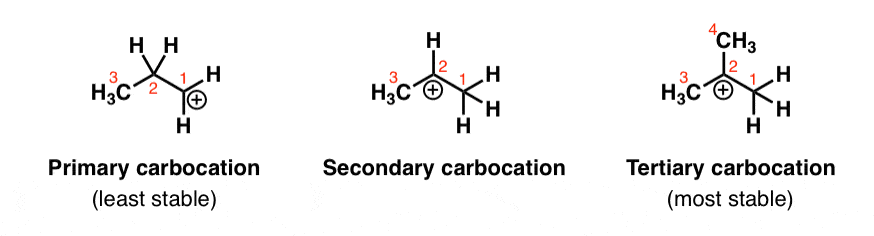
Stability of carbocation intermediates.
The lightest allylic carbocation 1 is called the allyl carbocation.
An allylic system has a minimum of 3 carbons.
In the first mechanism step the alkyne is protonated by hydronium ion a strong acid to produce a resonance stabilized secondary vinylic carbocation shown in red.
A vinylic carbocation which has an empirical formula of c h is a carbocation that has a positive charge only on the alkene carbon atom.
We know that the rate limiting step of an s n 1 reaction is the first step formation of the this carbocation intermediate.
The allylic carbon and the nearby double bond.
Heterolytic bond cleavage results in the ionization of a carbon atom and a leaving group in the starting compound the carbon atom is sp 3 hybridized.
See also primary allylic carbocation secondary allylic carbocation tertiary allylic carbocation.
The true structure of the conjugated allyl carbocation is a hybrid of of the two resonance structure so the positive charge is delocalized over the two terminal carbons.
It provides plenty of examples including allylic and vinyli.
For example in s n 1 mechanism the carbocation forms in the first step by the loss of the leaving group.
An allylic carbon is one that is directly attached to a pi bond.
Carbocation stability resonance rearrangement allylic vinylic examples organic chemistry duration.
The organic chemistry tutor 103 594 views 15 37.